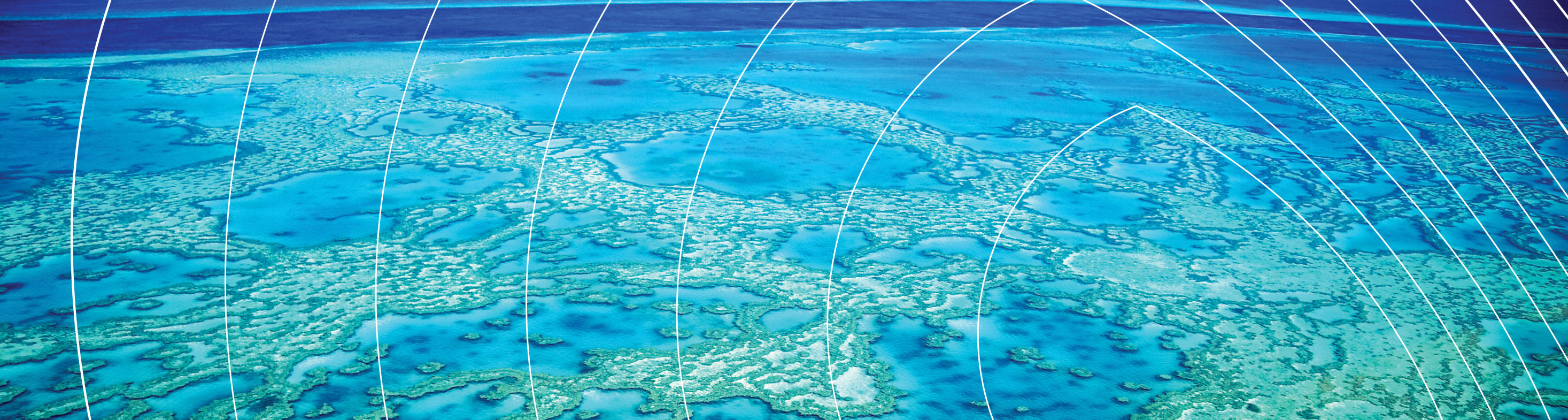

CASE STUDY: Mapping coral type and coral bleaching with aerial robots (drones)
Case Studies
Boeing Australia – Where humans and automation work together
Since the 2008 establishment of Boeing’s advanced research and development unit …
IR4 – Mass communication via robotic automation
IR4 is an early revenue technology company that is setting global benchmarks in …
Kalmar – AutoStrad Terminal Solution
Within the next 10-15 years many of the major stevedores will automate and the …
Wide area surveillance of the oceans requires a diversity of solutions …
Rio Tinto’s fleet of autonomous haul trucks have moved more than 1 billion tonnes of …
Share this story
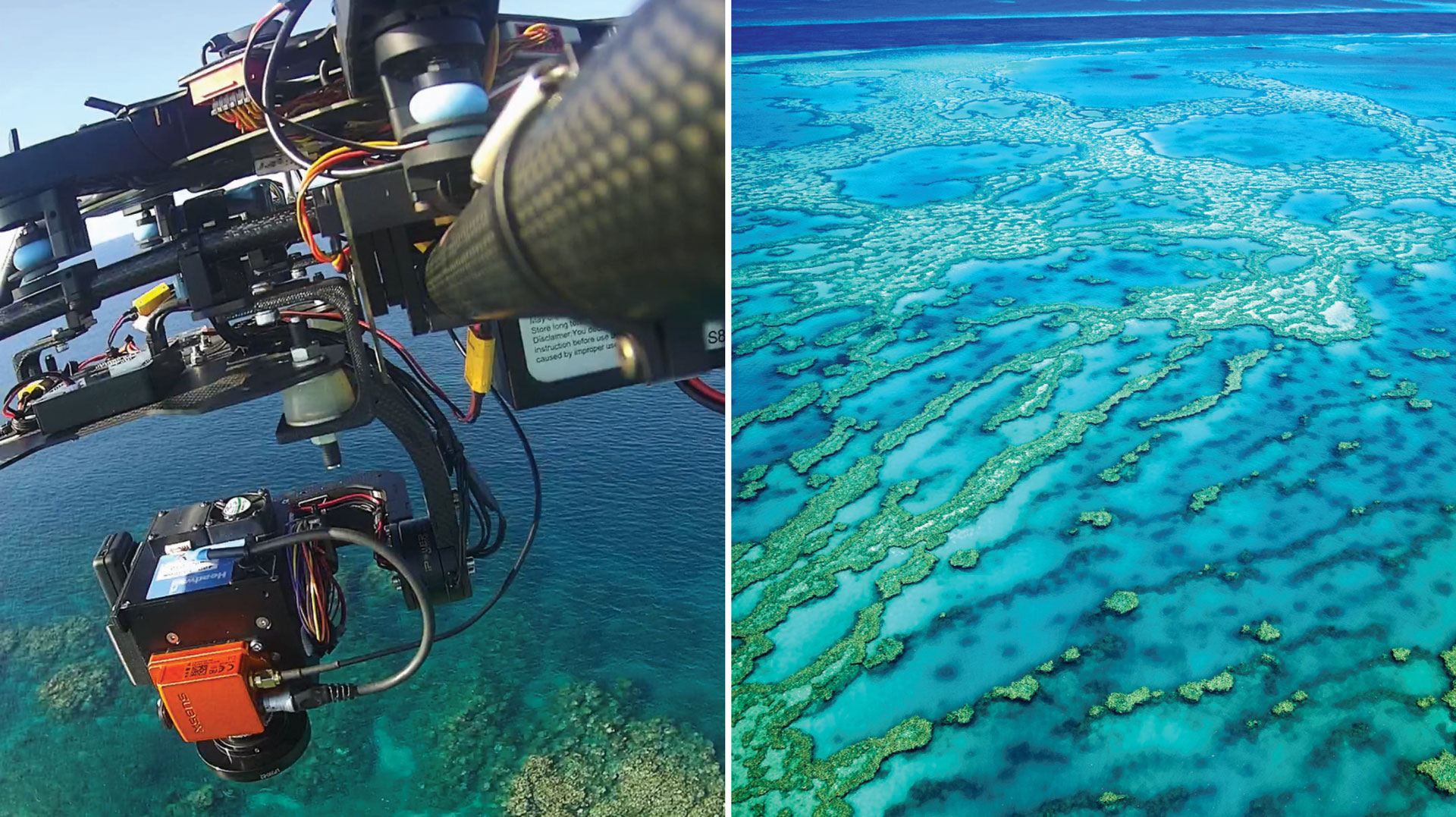
Advanced, miniature cameras on drones are capturing details of landscapes that have previously been invisible. QUT researchers are using them to fly low over reefs, capturing almost 100 times the colours captured by standard cameras.
“High-altitude surveys of reefs may lack the resolution necessary to identify individual corals or bleaching effects”, says Associate Professor Felipe Gonzalez, who is leading a team of researchers and unmanned aerial systems (UAS) engineers from QUT in a partnership project between QUT and the Australian Institute for Marine Science (AIMS).
“Normal cameras record images in three bands of the visible spectrum –– red, green and blue –– and mix those bands together to create colours as humans see them. A hyperspectral camera captures 270 bands in the visible and near-infrared portions of the spectrum, which provides far more detail than the human eye can see. Since we’re flying it on small UASs –– commonly known as drones –– at 30-100m over the water, we can get an incredibly high resolution,” Felipe says.
The team has used the drones over Western Australia’s Ningaloo Reef and collected vision from the Great Barrier Reef while AIMS conducted complementary underwater surveys.
QUT is now working on building underwater housing for a hyperspectral camera so the technology can be used in marine robots.
“The huge amount of information we can get will allow us to classify coral species, sand and algae, or coral bleaching based on unique spectral signatures, which act much like fingerprints,” Felipe says.
Researchers are building artificial intelligence algorithms to automatically recognise and classify the signatures, so these can be added to a database for future research. This kind of analytic software could also be used in detecting invasive plants and crop diseases.

Trending Article
An Australian university (ANU) has been the first to trial intelligent drones for automated inspection of solar power plants.
The project is an industry-researcher collaboration funded by the Australian government’s Australian Renewable Energy Agency (ARENA) developing a cost-effective robotic inspection system…

ANCA – Australia’s largest user of industrial robots
ANCA is an Australian company, founded in Melbourne in 1974, now with offices...
BIA5 Innovation Robotics and customers
BIA5 Pty Ltd is a start-up company that specialises in designing, manufacturing...
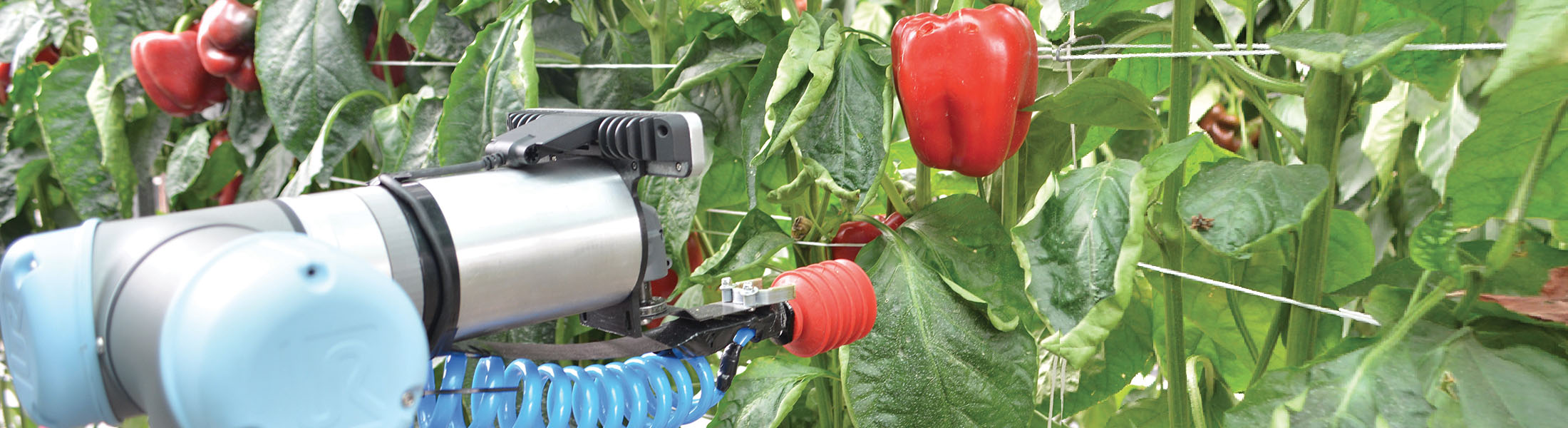

Harvey - the capsicum-picking robot
The horticulture industry in Australia has a gross value of more than $AU8...
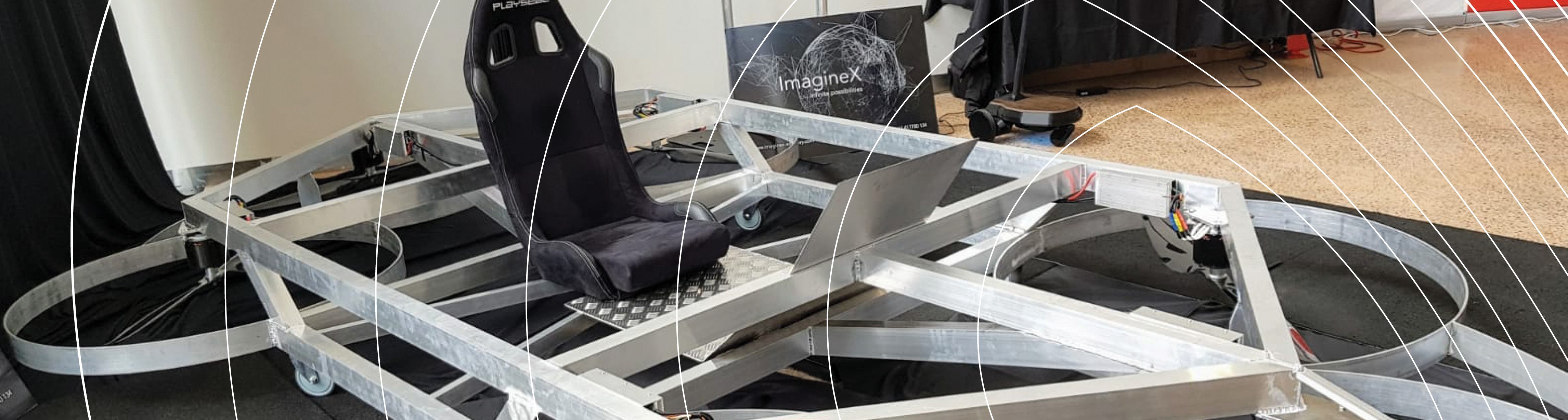

Pegasus Alpha – Flying car
In the back streets of Brisbane, two brothers with a passion for the automotive industry had a feeling that the future is vertical.
